The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex biological system that plays an important role in maintaining your body’s internal balance. Despite its importance, many people don’t know a whole lot about it.
Understanding the ECS can allow us to better understand how our bodies function and what cannabis does when it interacts with this system.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is a network of receptors, molecules (called endocannabinoids), and enzymes that are found throughout the body.
It was discovered in the early 1990s by researchers who were studying THC. The ECS plays an important role in regulating different physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, immune response, and more.
Components of the Endocannabinoid System
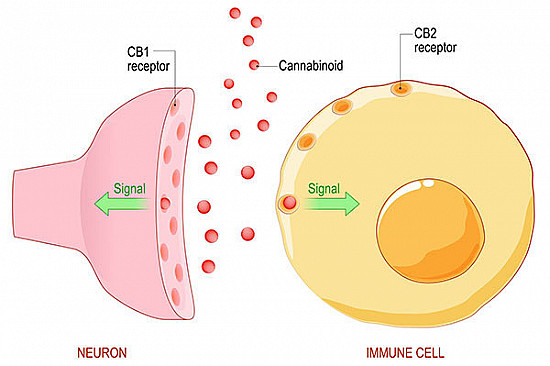
Cannabinoid Receptors: These receptors are located on the surface of cells and are involved in signaling within the ECS. The two primary receptors are CB1 and CB2:
Endocannabinoids: These are naturally occurring compounds that bind to cannabinoid receptors. The two most well-known endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Enzymes: These are responsible for synthesizing and breaking down endocannabinoids. The primary enzymes are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), which breaks down 2-AG.
Why is the Endocannabinoid System Important?
The ECS is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, which is the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment, despite external changes. By interacting with various physiological processes, the ECS helps to ensure that our bodies function optimally. Some of the important roles of the ECS include:
Understanding the ECS is essential because it provides insight into how our bodies maintain balance. This knowledge can also guide the development of new therapies for a range of conditions, from chronic pain to mental health disorders.
How Cannabis Interacts with the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabis contains a number of different compounds, including cannabinoids like THC and CBD, that interact with the ECS. These interactions can affect both your body and mind in a lot of different ways.

THC and the ECS
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. It mimics anandamide (which your body naturally creates) by binding to CB1 receptors in the brain. This produces the characteristic “high” associated with cannabis use.
THC can also interact with CB2 receptors, influencing immune responses and inflammation. However, THC’s binding to CB1 receptors is responsible for most of its psychoactive effects, including euphoria, altered perception, and increased appetite.
CBD and the ECS
Cannabidiol (CBD) is another major cannabinoid found in cannabis, but it interacts with the ECS in different ways then THC does.
CBD does not bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors. Instead, it influences the ECS by inhibiting the enzymes that break down endocannabinoids, leading to increased levels of anandamide and 2-AG.
Additionally, CBD interacts with other receptors, such as serotonin and vanilloid receptors, which can contribute to its effects on mood, pain, and inflammation. CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce a “high,” but it can have therapeutic effects, including reducing anxiety, alleviating pain, and providing anti-inflammatory benefits.
The Therapeutic Potential of Influencing the ECS
Given the ECS’s role in various physiological processes, targeting this system with cannabis or other compounds holds significant therapeutic potential in a number of different way, such as:

Understanding the ECS key to understanding how cannabis interacts with our bodies and why it can have such diverse effects. As research into the ECS continues, it opens the door to new therapeutic possibilities for treating a number of different conditions.
Whether you are a cannabis enthusiast, just starting out or someone interested in the potential medical benefits of cannabis, a deeper understanding of the endocannabinoid system is crucial for appreciating the impact that cannabis can have on our health and well-being.
Check out our online menu to see all that we have to offer as well as our specials page to see all the ways you can save!